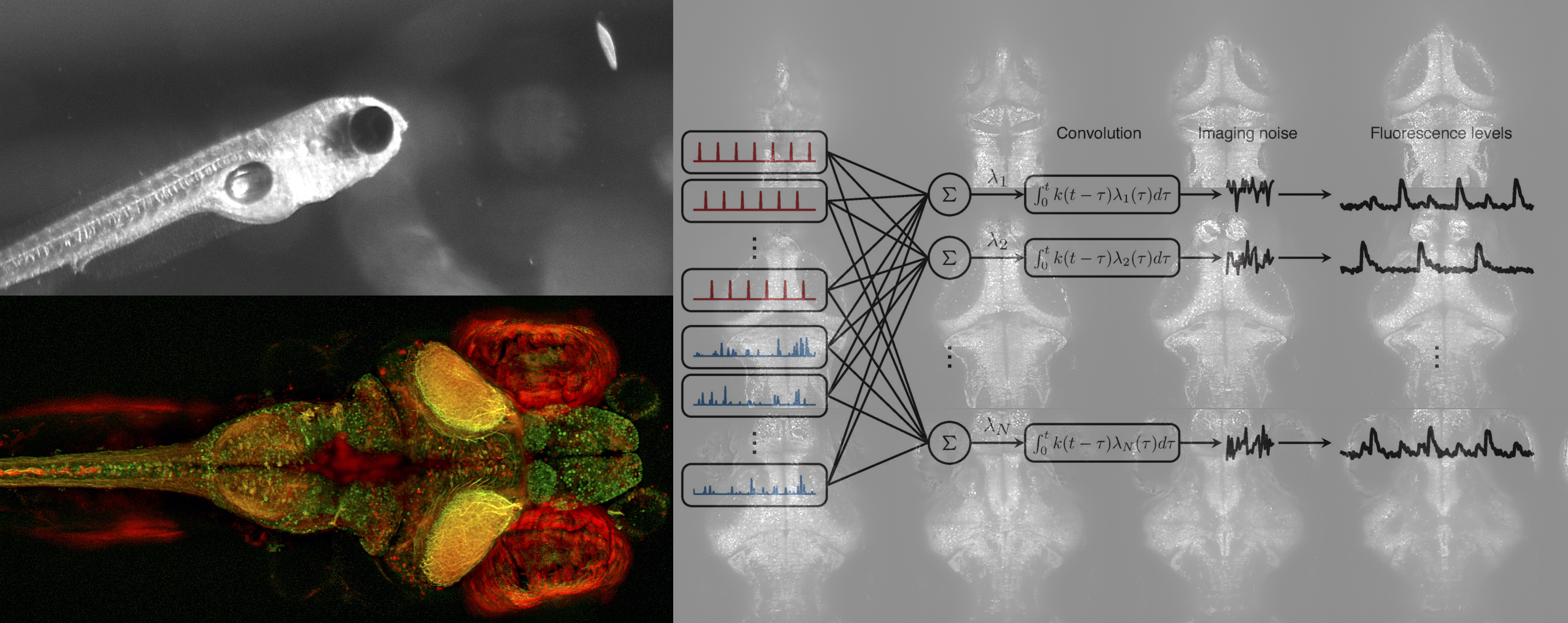
Neural assemblies and calcium imaging data
To help us
understand our data we often develop new
computational models and methods. Some recent examples
are as follows. We also recently reviewed
computational methods for analyzing
behavioral data here.
-
Calcium Imaging Latent Variable Analysis (CILVA). In two papers here and here
we developed a statistical model of the
interaction between spontaneous and evoked
activity in calcium imaging data, based on
the idea that spontaneous activity can
often be accurately represented by a small
number of latent (unobserved)
factors. Using statistical inference
procedures we simultaneously derived from
the data both the structure of these
latent factors and neural receptive
fields. This allows us to decouple
spontaneous from evoked activity,
providing the opportunity to study each in
relative isolation.
-
Detecting neural assemblies in calcium imaging data. Activity
in populations of neurons often takes the
form of assemblies, where specific groups
of neurons tend to activate at the same
time. However, in calcium imaging data,
reliably identifying these assemblies is a
challenging problem. In this paper in
BMC Biology we compared several recently proposed
assembly-detection algorithms, and
demonstrated leading performance for a
graph-clustering algorithm that we adapted
for this problem.
-
Emergence of spontaneous assembly activity in developing neural
networks without afferent input. In this paper we showed that a recurrent
network of binary threshold neurons with
initially random weights can form neural
assemblies based on a simple Hebbian
learning rule, without any afferent
input. This helps us understand our
experimental results in this paper where such assemblies arose even
in dark-reared fish. Surprisingly the set
of neurons making up each assembly
continually evolves in the model, a kind
of representational drift.